User interface (UI) and user experience (UX) UI/UX designers are crucial in determining how people interact with websites, apps, and software in the modern digital world. UI/UX designers are in charge of producing seamless digital experiences, from simple navigation to eye-catching graphics. Technical proficiency, inventiveness, and empathy are all necessary for success in this fast-paced industry.
Introduction
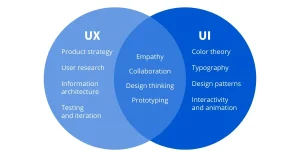
User interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design are critical components of every successful digital product or service in the modern digital age. The user’s interaction and engagement with any kind of interface, be it software, mobile, or the internet, is largely dependent on how well-designed it is. As a result, the need for knowledgeable UI/UX designers is still growing.
Essential Skills for UI/UX Designers
A broad range of skills are required of UI/UX designers in order to produce smooth and user-friendly experiences. These abilities fall into three primary categories: soft, technical, and creative capabilities.
Creative Skills
The core of any successful UI/UX design is creativity. A good sense of aesthetics and the natural ability to conceptualize and transform ideas into visually appealing designs are prerequisites for designers. It takes expertise with graphic design software, such as Adobe Creative Suite, to produce wireframes, prototypes, and mockups.
Technical Skills
UI/UX designers need to be skilled in a variety of technical areas in addition to having a creative flare. Understanding coding languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript helps designers work well with developers and comprehend the limitations of implementation. To create interactive prototypes and test design concepts, it’s also essential to have experience with prototyping tools such as Sketch, Figma, or Adobe XD.
Proficiency in Design Software
Proficiency in Adobe XD, Sketch, or Figma design software is essential for UI/UX designers to produce visually appealing prototypes and interfaces.
Understanding of Coding Languages
Although not always required, having a solid understanding of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript can help designers work more effectively with developers to make their ideas come to life.
Knowledge of Prototyping Tools
Creating interactive prototypes that mimic the user experience requires familiarity with prototyping tools like InVision or Proto.io.
Soft Skills
Apart from technical and creative skills, successful UI/UX designers possess strong soft skills that facilitate effective communication and collaboration. These include:
-
Communication: The ability to communicate clearly is essential for presenting design thoughts, getting feedback, and comprehending client requirements.
-
Empathy: By developing an understanding of end consumers, designers may produce solutions that are specific to their requirements and tastes.
-
Problem-solving skills: To improve the user experience, UI/UX designers need to be skilled at spotting usability problems and coming up with creative fixes.
-
Time management: In the fast-paced field of UI/UX design, meeting project deadlines and effectively handling several responsibilities are critical.
Understanding User Needs
It takes empathy for consumers on the part of designers to create UI/UX experiences that work. To address their wants and pain issues, this entails performing user research, obtaining feedback, and comprehending user behavior to develop solutions.
Proficiency in Design Tools
Proficiency in multiple design tools, including Adobe XD, Sketch, Figma, and InVision, is a requirement for UI/UX designers. By effectively using these tools, designers can convert ideas into realized designs by producing wireframes, prototypes, and mockups.
Visual Design Skills
For UI/UX designers, aesthetic sensibility is vital. They need to be well-versed in layout concepts, color theory, and typography to design aesthetically pleasing interfaces that improve usability and user engagement.
Also Read : Pros and Cons of Using AI in Education
Prototyping and Wireframing
Prototyping and wireframing are core components of UX/UI design. Before going on to high-fidelity designs, designers should be adept at converting concepts into low-fidelity prototypes to test functionality and get user input.
Interaction Design
The main focus of interaction design is on user interaction with digital products. To guarantee a positive user experience, UI/UX designers must create simple, straightforward interactions with components like buttons, menus, and navigation systems.
User-Centered Design
The wants and preferences of users must be prioritized throughout the design process by UI/UX designers who use a user-centered design approach. In order to continuously enhance the user experience, this entails carrying out usability testing and revising designs in response to user feedback.
Coding Skills
For UI/UX designers, it might be helpful to have a basic understanding of front-end development languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript; however, it’s not necessarily required. As a result, they are able to interact with developers more successfully and comprehend the technological limitations of their designs.
Design Skills
Graphic Design Fundamentals
Design principles like hierarchy, composition, and layout must be thoroughly understood to create aesthetically appealing interfaces.
Typography
Understanding typography principles and selecting the right typefaces may have a big impact on a design’s readability and visual attractiveness.
Color Theory
Comprehending the principles of color psychology and applying them skillfully can elicit feelings and direct user actions within an interface.
Collaboration and Communication
Product managers, marketers, developers, and other cross-functional teams frequently work together with UI/UX designers. Throughout the design process, it is crucial to have strong communication skills in order to receive input, align stakeholders’ goals, and effectively explain design concepts.
User Research Skills
Conducting User Interviews
Real users’ wants, preferences, and pain points must be understood by UI/UX designers through the collection of their insights.
Creating User Personas
Creating user personas aids designers in understanding their target market and creating designs that are tailored to their particular requirements.
Analyzing User Feedback
Continuous feedback loops are the foundation of iterative design, which uses real user interactions and insights to hone and improve the user experience.
Interaction Design Skills
Creating Intuitive User Interfaces
To guarantee a flawless user experience, designers must concentrate on developing interfaces that are simple to use and intuitive.
Wireframing and Mockups
Before beginning development, designers can refine the functionality and layout of a design by wireframing and making mockups of their ideas.
Usability Testing
By testing designs with actual users, usability concerns can be found early in the process, and design decisions can be verified.
Problem-Solving Abilities
The nature of UI/UX design is problem-solving. Designers need to be skilled at recognizing the challenges that users face, deciphering complicated issues, and coming up with creative fixes that improve usability and user happiness.
Adaptability and Continuous Learning
With the development of new technologies and shifting consumer expectations, the field of UI/UX design is always developing. For designers to stay competitive in the profession, they need to show that they are willing to learn new skills and adapt to changing trends in the industry, as well as tools and best practices.
Empathy and User Advocacy
The foundation of UI/UX design is empathy. In order to build inclusive and accessible digital experiences for a variety of audiences, designers must embrace user-centric design principles and speak up for the needs and preferences of their users.
Attention to Detail
Rigorous attention to detail is essential for UI/UX designers to ensure that every element of the design, from font to spacing, is well-polished and consistent. Inconsistencies in design can negatively impact the overall user experience, highlighting the significance of accuracy in design implementation.
Critical Thinking Skills
UI/UX designers need to be critical thinkers in order to assess design solutions, assess challenges, and make well-informed decisions all during the design process. To achieve the best results, designers must be able to predict user wants and potential usability problems, iterating designs as needed.
Importance of UI/UX Skills in Design
Good UI/UX design has a direct impact on user happiness, engagement, and retention; it is not just about aesthetics. A well-designed interface improves usability, lowers friction during user interactions, and eventually helps a product or service succeed. If companies want to stand out in crowded markets and provide great user experiences, they must invest in talented UI/UX designers.
Tools of the Trade
Many tools are used by UI/UX designers to expedite their work and realize their design concepts. These are essential tools for any UI/UX designer, from wireframing and prototyping to user testing and teamwork.
-
Sketch
-
Adobe XD
-
Figma
-
InVision
-
Axure RP
-
Marvel
-
Zeplin
-
UserTesting
-
Balsamiq
-
Miro
Time Management and Prioritization
UI/UX design projects frequently face conflicting priorities and short timeframes. To efficiently prioritize activities, assign resources, and fulfill project goals while retaining design quality and integrity, designers need to be highly skilled time managers.
Portfolio Development
Establishing a robust portfolio is crucial for exhibiting UI/UX design proficiencies and drawing in prospective employers or customers. In order to showcase their creativity, problem-solving skills, and the influence of their designs on user experiences, designers should organize their portfolios to feature just the best pieces.
Conclusion
UI/UX designers need to possess a wide range of abilities, including technical know-how, creativity, empathy, and critical thinking. Aspiring designers may produce memorable digital experiences that enthrall people and propel business success by learning five crucial skills and keeping up with industry developments.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
-
Is coding knowledge necessary for UI/UX designers?
Basic coding knowledge is not required; however, it can help UI/UX designers better grasp the technical aspects of their ideas and work together with developers.
-
How important is user research in UI/UX design?
Understanding user demands, behaviors, and preferences is essential for UI/UX designers to develop solutions that effectively solve real-world issues. This is why user research is so important to the field.
-
What role does empathy play in UI/UX design?
Understanding and sympathizing with users’ viewpoints enables designers to create more intuitive and user-centric design solutions, which is why empathy is crucial to UI/UX design.
-
How can UI/UX designers stay updated on industry trends?
UI/UX designers can read trade journals and blogs, take part in online communities, attend conferences, workshops, and webinars, and so on, to remain current on industry trends.
-
What makes a strong UI/UX design portfolio?
An impressive UI/UX design portfolio includes a range of projects that highlight the designer’s inventiveness, aptitude for solving problems, and understanding of how their designs affect user experiences. Case studies that illustrate each project’s design methodology and reasoning ought to be included as well.


GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings